For years, the Federal Bureau of Investigation has been unraveling what it asserts is a scam perpetrated by agents of North Korea, which used fake companies employing real IT workers to funnel money back to the regime’s military.
An American company played a key role in creating shell companies used as part of the scheme, a WIRED review of public records shows. Elected officials are now contemplating addressing loopholes in business-registration law that the scheme exposed.
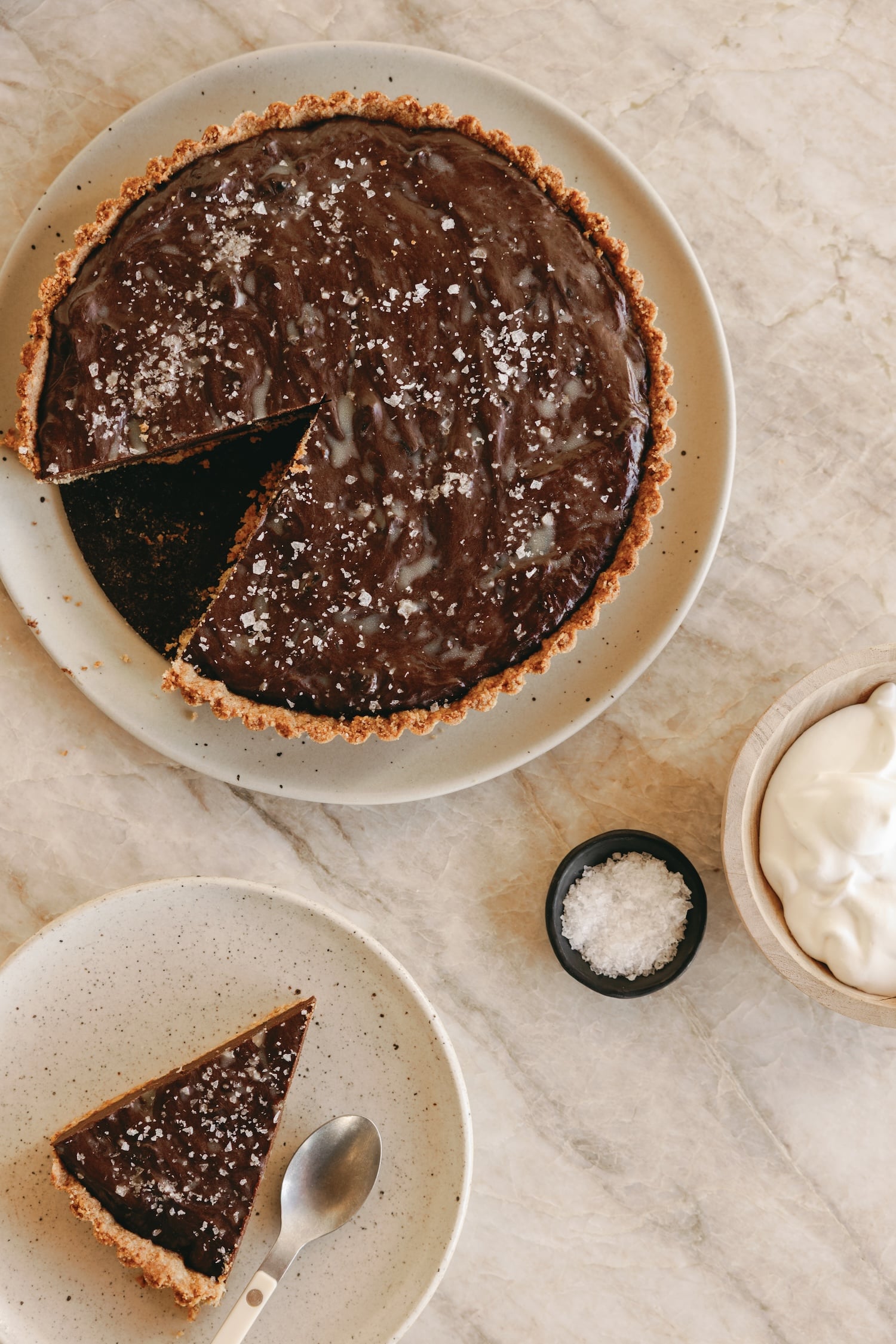
In May, Wyoming secretary of state Chuck Gray revoked the business licenses of three companies linked to the North Korean scam: Culture Box LLC, Next Nets LLC, and Blackish Tech LLC. Gray said his office made the decision after receiving information from the FBI and conducting an investigation.
“The communist, authoritarian Kim Jong Un regime has no place in Wyoming,” Gray said in a May press release.
The companies posed as legitimate operations where businesses could hire contract workers to perform IT solutions, complete with fake websites featuring smiling photos of apparent employees. The companies all had one thing in common: Their incorporation documents were filed by a company called Registered Agents Inc., which says its global headquarters is in Sheridan, Wyoming.
Registered Agents, which provides incorporation services in every US state, takes the practice of business privacy to the extreme, and regularly uses fake personae to file formation documents with state agencies, a WIRED investigation previously found.
Culture Box LLC, one of the companies that Gray and the FBI linked to North Korea, listed “Riley Park” as the name of a Registered Agents employee on documents submitted to the Wyoming secretary of state. Park, according to several former employees of Registered Agents, is a fake persona that the company regularly used to file incorporation documents.
In a statement provided to WIRED, Registered Agents wrote, “The Wyoming Secretary of State dissolved the entities and we initiated the 30-day process to resign as their agent in mid-May. Ours and Wyoming’s processes to identify bad actors works. It strikes the best balance of individual privacy and business transparency supported by an entire ecosystem that cares about supporting entrepreneurs while rooting out the small percent of scammers.” The FBI’s St. Louis office, which led the investigation, did not respond to a request for comment.
The North Korean operation worked like this: Agents of the regime created fake companies purporting to be legitimate firms offering freelance IT services. Workers hired by North Koreans, or North Koreans themselves, would then perform legitimate contractor work, often using assumed identities.
In some instances, Americans would set up low-cost laptops with remote-access software, allowing North Korean workers to perform freelance IT work while appearing to use American IP addresses. The FBI referred to these Americans as “virtual assistants.”
The payments for the IT work were eventually funneled back to North Korea—where, the Department of Justice asserts, it was directed to the country’s Ministry of Defense and other agencies involved in WMD work. The scheme was so expansive that any company that hired freelance IT workers “more than likely” hired someone involved in the operation, according to FBI agent Jay Greenberg.