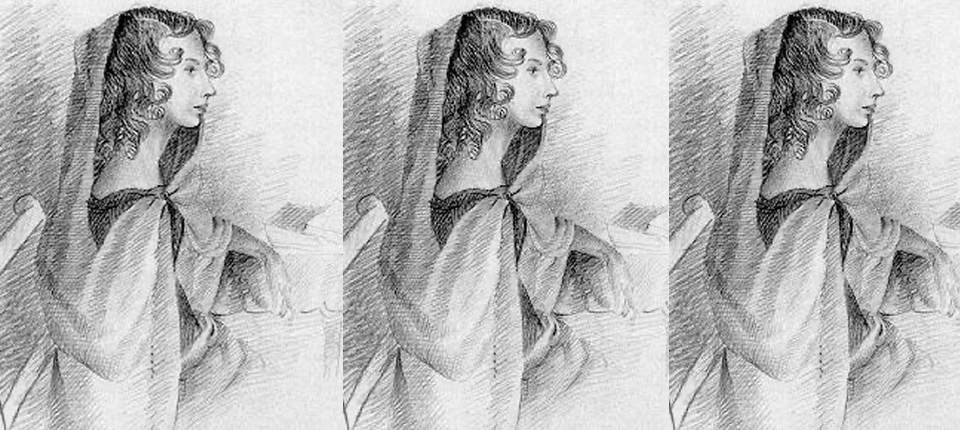
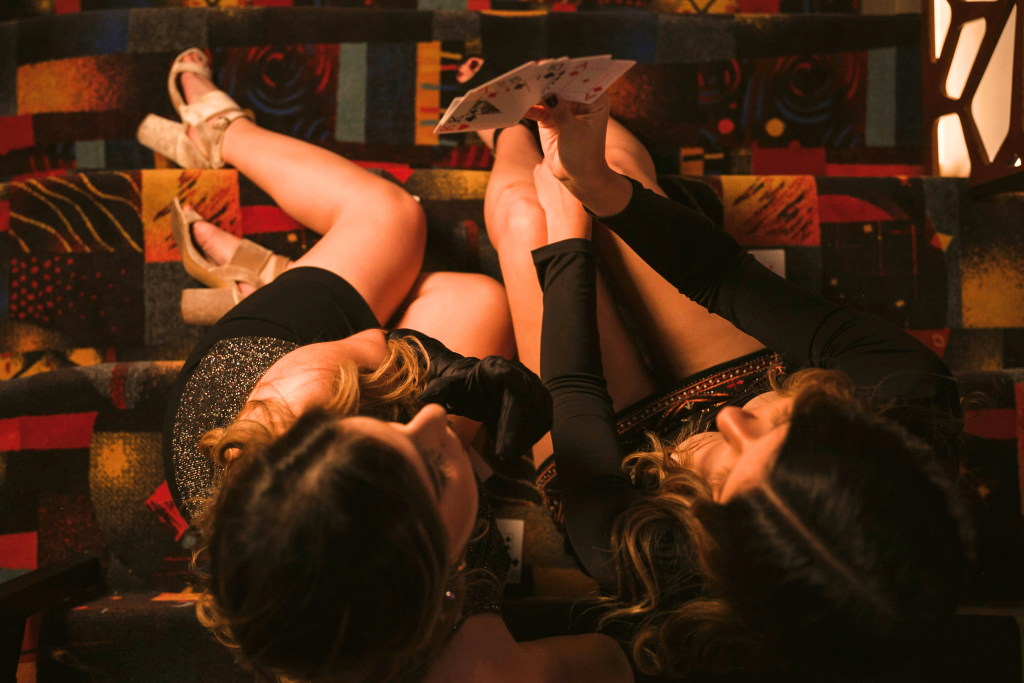
A moving exhibition at Bletchley Park shows women’s crucial contribution to the success of the UK’s wartime intelligence centre
Humans
11 May 2022
THROUGH movies like Enigma and The Imitation Game, we think we know all about Bletchley Park, the UK government intelligence centre in Buckinghamshire that broke the codes and cyphers of the Axis powers and changed the course of the second world war. But there are, it turns out, still plenty more stories to tell.
The Intelligence Factory, a permanent new exhibition on the Bletchley Park site, which has been a museum since 1993, mostly steers clear of the achievements of the likes of Alan Turing. Instead, it seeks to recreate the unsung work, also invaluable to the war effort, undertaken by the large and largely anonymous cast of more junior workers. This was predominantly young women, who enabled Bletchley to gather and disseminate “the product”, as it described its intelligence, to Allied forces and politicians.
Visitors can see historic objects – often in the rooms where they were used in wartime – such as a Hollerith tabulating machine and its punch cards, which became a stepping stone to modern computing. There are huge maps and charts on which analysts tracked shipping convoys in near real time, interactive elements to illustrate the problem-solving that took place, and impressive examples of early analogue data management, storage and visualisation systems – all of which have direct parallels today.
But The Intelligence Factory also features diaries, home movies and even teddy bears belonging to workers, mixing the intensely personal with the wider picture of ordinary people taking on an extraordinary task.
The sheer scale of the endeavour is overwhelming: you even enter through a large loading bay built to accommodate the delivery of 2 million punch cards every week to feed the Hollerith machines.
When war began, Bletchley was likened to a small university. It succeeded in cracking codes, but the sheer weight of information it received became ever more unmanageable. Over the years, it dramatically scaled up to something closer to a factory. By the end of the war, 9000 people were on site, 75 per cent of them women. Their work – such as punching those cards – was often mind-numbingly repetitive, and they had little or no idea where they fitted into the bigger picture.
They were also forbidden to speak about their work, even to colleagues. Unsurprisingly, morale was a major concern for Bletchley’s leadership, and its famous tennis courts as well as its concerts and societies were a stab at addressing the issues. But logistics were even more of a headache
Feeding, housing and transporting the workforce became as much a focus as the logistics of collating, sharing and making retrievable the vast swathes of information (all on paper) across the site. The exhibition shows both activities, with food playing a prominent role. A newfangled idea – the canteen, copied from the Kodak factory in Harrow – was introduced to improve efficiency.
Scattered across the exhibition are modern applications of ideas developed at Bletchley in the 1940s. These include an Encrochat phone used by criminal gangs, whose encryption was cracked by international crime agencies, and algorithms that identify suspicious shipping movements.
Another new exhibition on the site, The Art of Data, also explores data visualisation through strikingly visualised 21st-century uses, from heat maps tracking swimmers in an Ironman race to the movements of the local Milton Keynes Dons football team during a match.
Behind all this, the human element shines out, as it did in wartime. It was the quiet skills of organisation and resilience as well as genius minds and cutting-edge innovation that allowed Bletchley to succeed. In the end, The Intelligence Factory is a moving and inspiring story of a myriad small jobs being done by ordinary people that together amounted to something very special.
More on these topics: