Humans are sending ever more rockets up into space – bits of them falling back to Earth could result in casualties, unless action is taken
Space
11 July 2022
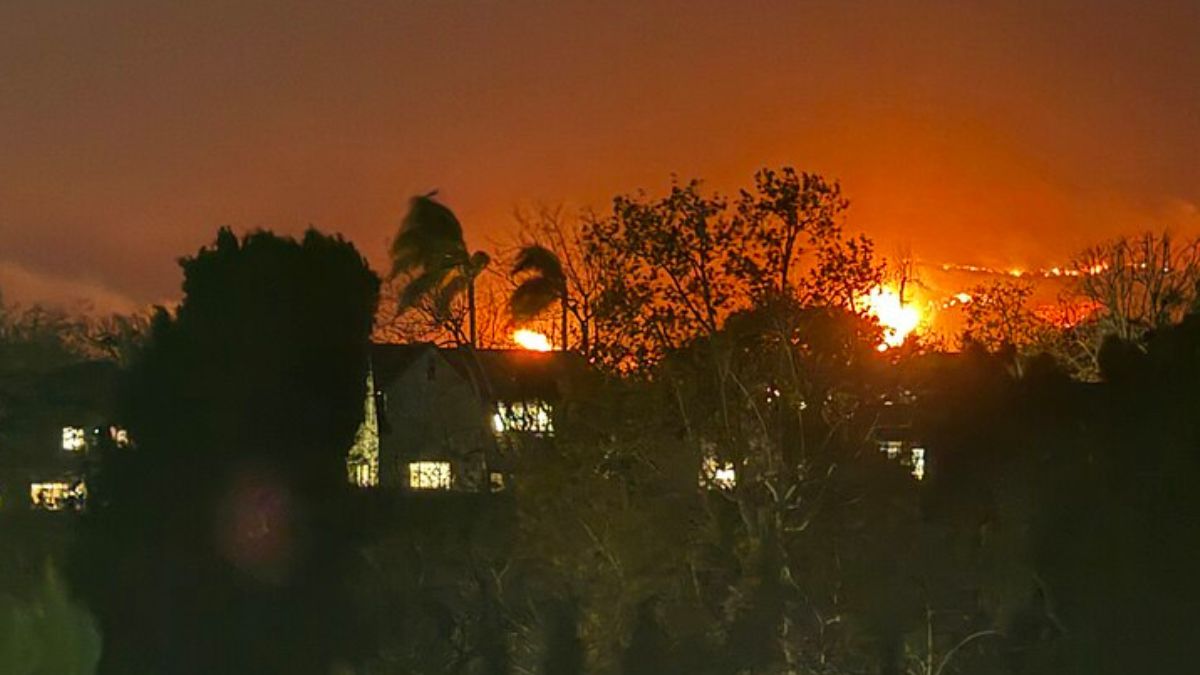
The wreckage of a Long March rocket that landed in Guizhou, China, on 31 December 2014 – fortunately, no one was hurt TPG/Getty Images
Pieces of rocket falling uncontrolled back into our atmosphere may cause casualties, unless action is taken to limit the risk they pose.
The number of rockets launched annually has been steadily increasing in recent years, with 135 successfully going up in 2021 – the record for a single year. Many of these launches involve discarding part of the rocket in space after a satellite that is being carried up is boosted into its desired orbit. The rocket parts often then fall back towards Earth, and more than 1000 rocket bodies are estimated to have uncontrollably re-entered the atmosphere in the past 30 years.
Much of this debris falls into the ocean, which covers more than two-thirds of our planet’s surface, but some ends up striking things on land. In May 2020, a 12-metre-long pipe suspected to originate from a Chinese rocket fell in a village in the Ivory Coast. In April 2022, another piece of debris reported to come from a Chinese rocket landed near a village in India. Wreckage of a Chinese Long March rocket also landed in Guizhou, China, in December 2014 (see picture above).
Now, Michael Byers at the University of British Columbia in Canada and his colleagues have calculated the danger that such falling debris poses. They say there is a 10 per cent chance of one or more casualties being caused by falling debris over the next decade, and the risk is disproportionately higher in low-income nations near the equator, where population densities are higher and more debris tends to fall because more rocket bodies travel over the equator.
“We think this has to stop,” says Byers, who wants rocket companies to be told to keep leftover fuel to target safe re-entries over uninhabited ocean regions. “We have modern rockets that can avoid uncontrolled re-entries, rather than playing Russian roulette with the Ivory Coast and India. Who’s to say the next piece won’t come down in central Mumbai?”
Jonathan McDowell at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics says rocket stages discarded in orbit are a large problem, particularly with regards to space debris. “When you have stages left in orbit, there’s a collision risk,” he says. There is also a danger such stages can explode because of fuel left on board. “The only way to make sure your rocket isn’t going to blow up is to de-orbit it,” says McDowell.
In the event that debris from a rocket does cause damage or casualties on Earth, Ram Jakhu at McGill University in Montreal, Canada, says legal action can be taken under the United Nations’s Liability Convention of 1972. Only one such case has been seen before, when Canada was awarded CAN$3 million (US$2.3 million) from the Soviet Union in 1981 after a Soviet satellite crashed in the country in 1978, but the convention could be used again.
“I have no doubt there is going to be another serious incident,” says Jakhu. “There’s a strong probability of hurting somebody or damage to property.”
Some organisations, like SpaceX, are already landing the lower part or first stage of their rockets back on Earth following a launch. Yet second stages – used to boost satellites into their final orbits – are still regularly left to drift in space, rather than being brought back through Earth’s atmosphere into uninhabited regions of the ocean, often because the rockets carry the precise amount of fuel to do their job of launching satellites rather than leaving some for a controlled return journey.
SpaceX and the China National Space Administration didn’t respond to a request for comment.
“The goal is to have international agreement to phase out uncontrolled re-entries,” says Byers. “Some older rocket designs may need to be put out of service or modified.”
Journal reference: Nature Astronomy, DOI: 10.1038/s41550-022-01718-8
Sign up to our free Launchpad newsletter for a voyage across the galaxy and beyond, every Friday
More on these topics: