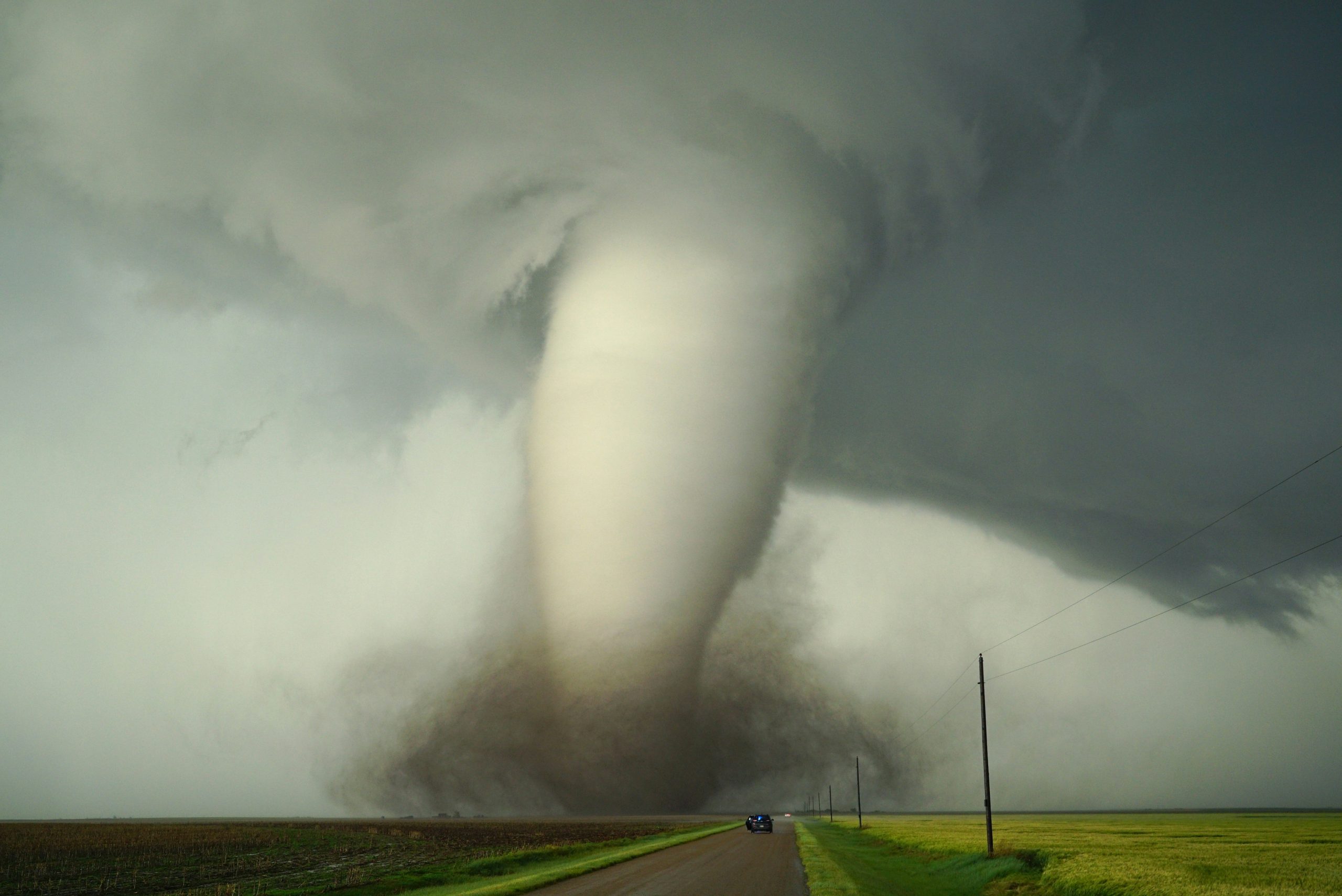
People across the UK and US may glimpse a special light show tonight
Marc Hilton/iStockphoto/Getty Images
The aurora borealis, or northern lights, are expected to be more active than they have in decades the evening of 10 May, according to an announcement by the US National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). They could be visible as far south as Alabama in the US and Scotland in the UK. This marks the first severe geomagnetic storm watch from NOAA since 2005.
This shimmering green, purple and red glow in the sky occurs when charged particles from the sun smash into Earth’s atmosphere. The sun emitted several huge plumes of particles, called coronal mass ejections (CMEs) between 8 and 9 May, and they are expected to reach Earth on 10 and 11 May.
When these particles reach Earth, many of them are deflected by the planet’s magnetic field. But the field is weaker around the poles, so some of them manage to sneak in and hit the atmosphere, where they impart energy to its constituent gas molecules. When these molecules re-emit the energy, it comes out as the light that we see as the aurora. The colour of the aurora depends on what type of gas was hit and where in the atmosphere it is located – green, the most common colour, comes from oxygen molecules around 120 to 180 kilometres up in the air.
The more powerful the CME, the more particles sneak into the atmosphere and the brighter and bigger the aurora is. The CMEs that just blasted off the sun are more powerful than any that have hit Earth since January 2005. Solar storms this powerful can even disrupt satellites and the electrical grid by releasing powerful currents that may damage their components.
To see the aurora, you need to be as far as possible from any major light pollution – it can be impossible to spot even an incredibly powerful aurora from urban locations. Once away from city lights, let your eyes adjust to the darkness and look to the northern sky.
In the US, people may see the aurora by late 10 May or early 11 May over most of the northern half of the country, and potentially as far south as Alabama to northern California, according to NOAA. As for the UK, the Met Office predicts it will be visible across the northern half of the country toward the end of 10 May or early 11 May – but there is a chance the entire country could glimpse it.
Auroras may appear in photographs as bright, shimmering sheets of light, but to the human eye, without the power of a long exposure time, they tend to look more like a faint, shifting green glow. For those that live outside of the Arctic Circle, this may be the clearest auroral show in 19 years.
Topics:


















































.jpg)



