More than 40 years and 1,000 or so patents after selling his first company, AutoSyringe, to healthcare giant Baxter, Dean Kamen still gets a charge describing breakthrough innovation. It’s been five years since his organ fabricating project ARMI (Advanced Regenerative Manufacturing Institute) divided critics.
The project made more waves early last month, at the CNN-hosted conference Life Itself. Kamen paints the picture appearing on a panel at TC Sessions: Robotics today:
Doris Taylor, who moved up here from where she spent more than a decade in Texas, at the Texas Heart Institute, she gets on stage with a beaker. In the beaker is a miniature, pediatric-scale beating heart that was manufactured with induced pluripotent stem cells were put into a scaffold of preexisting organ. Within an hour of that presentation, Martine Rothblatt, the founder and chairman of United Therapeutics, is on stage and they roll out from backstage an almost surrealistic, lit from the top of the box. A panel opens, and what emerges out of the top of this platform is a scaffold of a human lung, that was printed, entirely printed at the smallest scale any printer has ever operated.
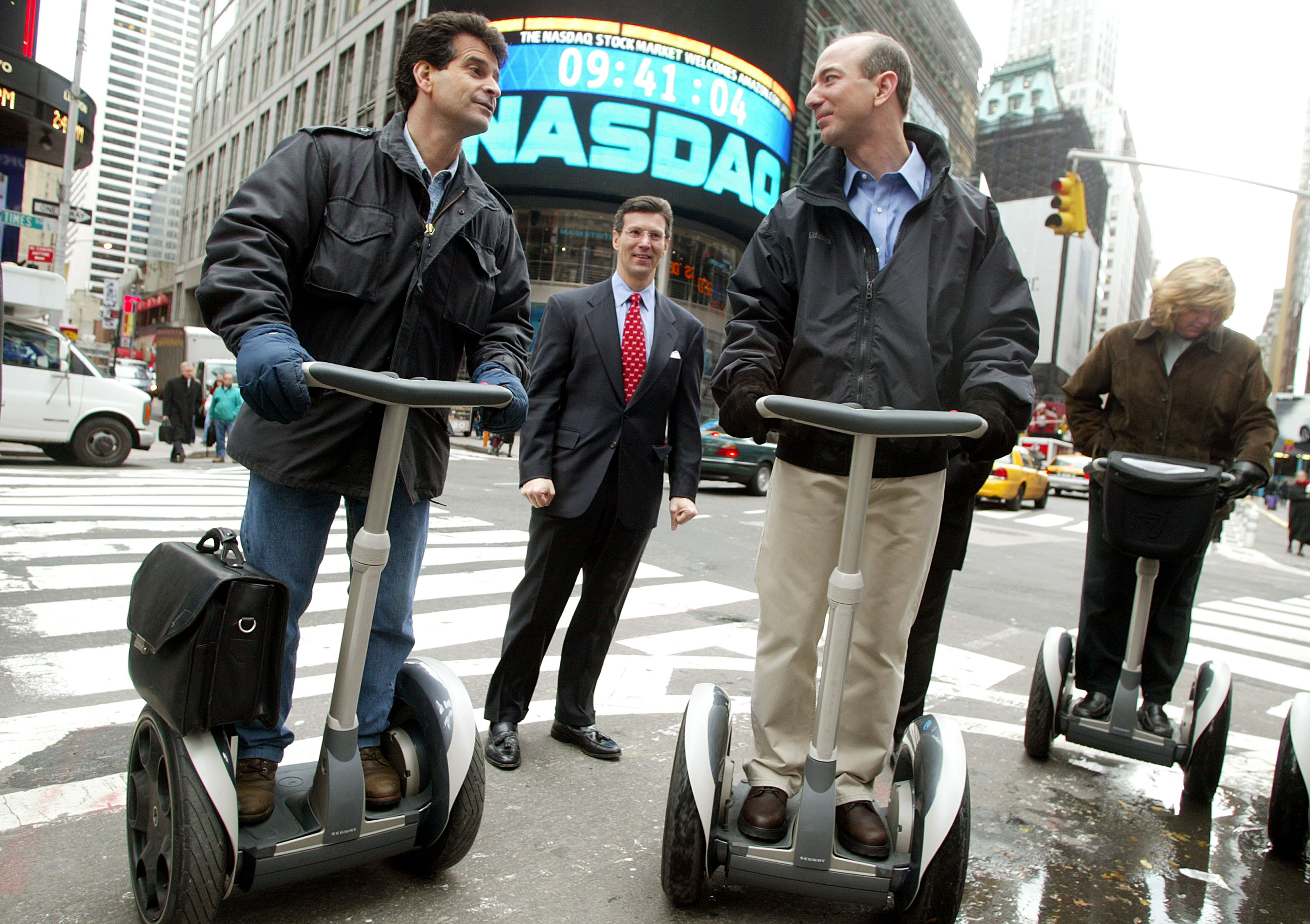

NEW YORK – NOVEMBER 18: (FILE PHOTO) Amazon.com CEO Jeff Bezos (R) stands on a Segway with Segway inventor Dean Kamen (L) and NASDAQ Vice Chairman David Weild (C) after opening the NASDAQ Stock Market November 18, 2002 in New York City. The Consumer Product Safety Commission announced September 26, 2003 that Segway LLC has recalled all 6000 Segways sold since March 2002 because of dangers associated with low batteries that may cause the human transporter to fall. (Photo by Mario Tama/Getty Images)
Kamen is first to admit, however, that the path to all success is paved with failure. The trick is learning the right lesson.
“What I’ve learned from failure is go back and decide was the fundamental goal wrong — that’s why it failed, you succeeded, but nobody needs this — or did the available technology and your systems integration and application have it wrong, in which case, you’ve now learned enough, go try again, go use a different approach,” Kamen explains. “Pick yourself up, try again, using a different approach. And it really doesn’t matter how many times you fall down. If you fall down five times, but you stand up six, it’s okay. And in the end, you only need a win every once in a while to keep your confidence up. And hopefully, to give you the resources to keep going even though inevitably you’ll have failures, let the projects fail, don’t let the people fail.”
These are among the fundamentals Kamen has attempted to infuse into FIRST, the education program he co-founded in 1989, with MIT professor Woodie Flowers. It is best known for the FIRST Robotics Competitions, which center around competitive builds of robots and other projects, bringing the teamwork and enthusiasm of sports to STEM education — subjects that might otherwise turn off students who traditionally encounter them in more formal and staid settings.
“Kids won’t go to class, or they’ll take math for 45 minutes between phonics and spelling, one day a week. But they’ll go after school for three hourse, every single day to get better at football or get better at basketball. So I said, ‘look, we’re not competing for the hearts and minds of kids with the science fair and the spelling bee, we’re competing with the things that they invest all of their time, energy and passion in. So let’s use that model — make it aspirational, make it after school. Don’t give them quizzes and tests, give them letters and trophies. Bring the school band and the mascots.”
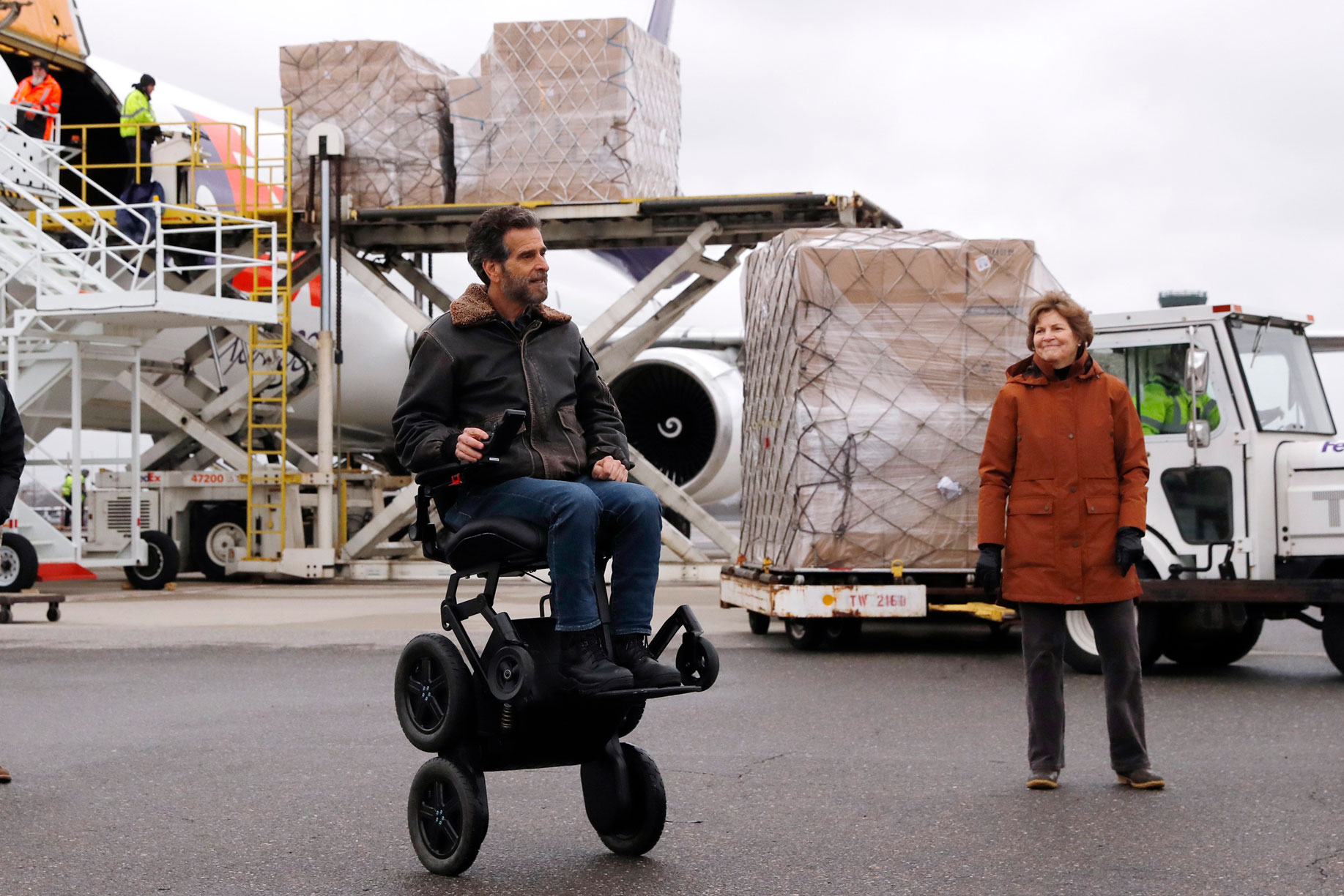

U.S. Sen. Jeanne Shaheen (D-NH), right, looks toward inventor Dean Kamen as over 110,000 pounds of personal protective equipment (PPE) from Shanghai, China, delivered to protect medical workers and first responders fighting the COVID-19 virus outbreak, is unloaded from a cargo plane at Manchester-Boston Regional Airport in Manchester, New Hampshire, Thursday, April 30, 2020. (AP Photo/Charles Krupa)
Perhaps the hardest-fought lesson of all, however, is understanding, accepting and even welcoming the fact that progress in technology and sciences means that one day your best work will be eclipsed.
“You have to be more than prepared for it. You have to be confident it will happen, and you have to celebrate it. I celebrate it more when it’s me that obsoleted the last thing I did, but if somebody else can obsolete it and if I get to a point where I need a better clinical solution than a dialysis machine or an insulin pump, if I can get to a place with somebody else’s technology to gave me a new organ or a prosthetic limb or something, I need to have a better quality of life, I will thank that person. And I hope I will return that favor by giving them something of value that we invented.”






















































![[Spoiler] Shot, Wes vs. Csonka [Spoiler] Shot, Wes vs. Csonka](https://www.tvinsider.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/fbi-international-408-vo-wes-1014x570.jpg)