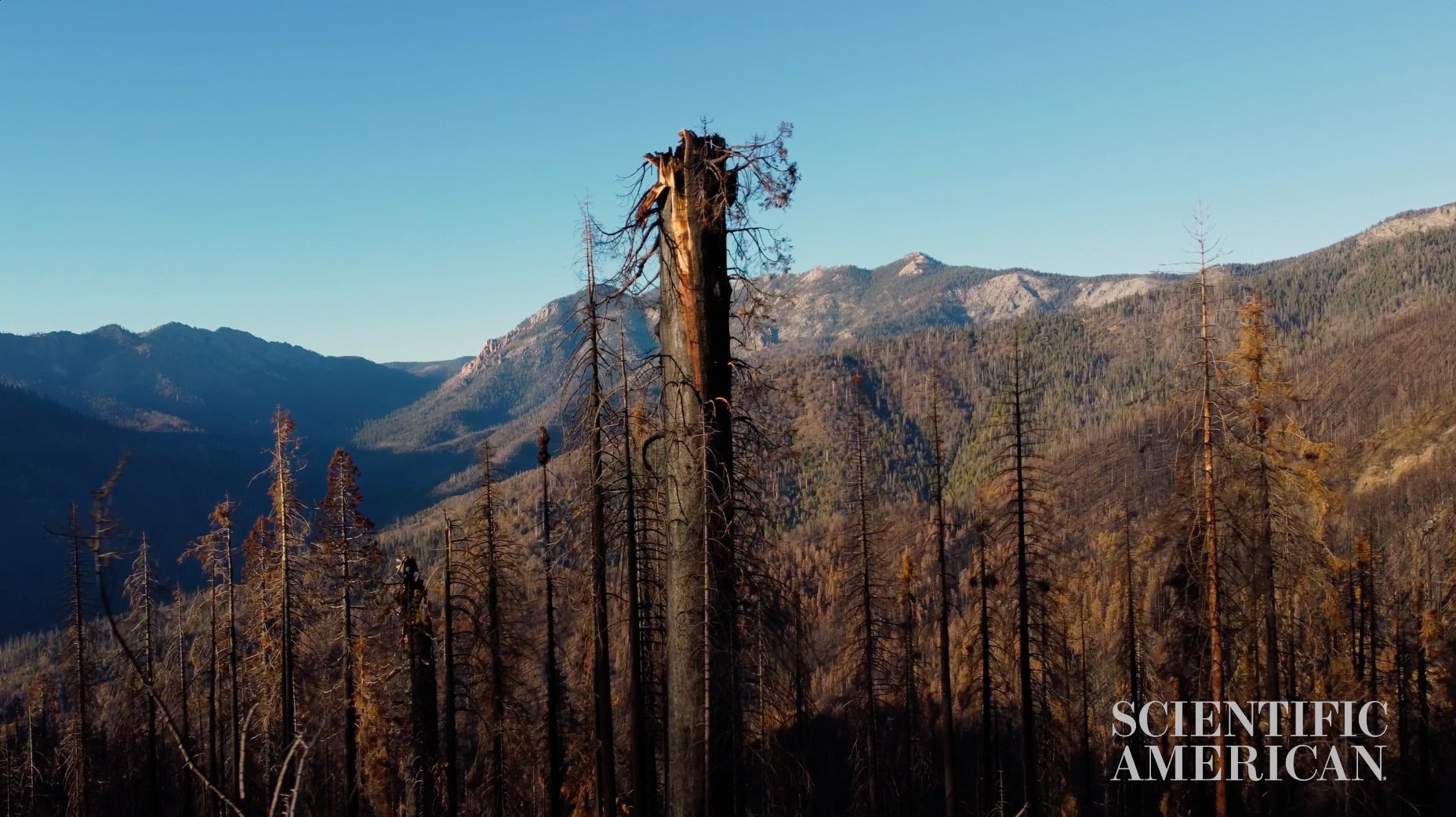
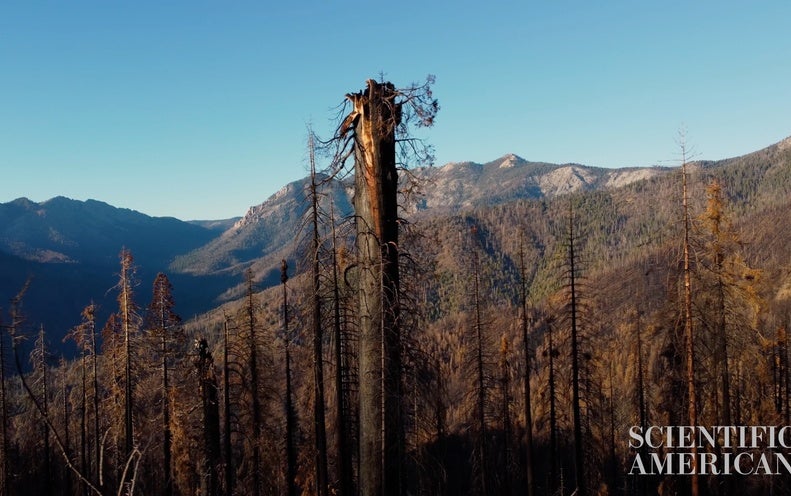
On a dead still November morning in the Sierra Nevada, two researchers walk through a graveyard of giants. Below their feet: a layer of ash and coal. Above their heads: a charnel house of endangered trees.
This is Alder Creek Grove, a once idyllic environment for a majestic and massive specimen: the giant sequoia. It is now a blackened monument to a massive wildfire—and humankind’s far-reaching impact on the environment. But these two researchers have come to do more than pay their respects.
Linnea Hardlund and Alexis Bernal, both of the University of California, Berkeley, are studying the effects of record-breaking fires such as the one that destroyed large swaths of Alder Creek Grove in the hopes that their findings will inform forest management that might preserve giant sequoias for future generations.
So far, those findings are grim: mortality is near 100 percent where the wildfires burned most intensely. Of the mighty trees that stood watch for thousands of years, only charred skeletons remain.
About a century of aggressive fire suppression and a warming, drier climate have created a perfect environment for unprecedented fire. On August 19, 2020, it came to the Giant Sequoia National Monument. The SQF Complex was two fires—the Castle and Shotgun fires—that burned for more than four months, affecting nearly 175,000 acres. And a preliminary report on the Castle Fire estimated that 10 to 14 percent of all living giant sequoias were destroyed.
Hardlund, who is also at the nonprofit Save the Redwoods League, and Bernal fear that, without scientifically informed intervention, such fires will continue to return to the Sierra Nevada—leaving the once proud guardians of the forest a memory and another casualty of our ecological failure.































![[Spoiler] Shot, Wes vs. Csonka [Spoiler] Shot, Wes vs. Csonka](https://www.tvinsider.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/fbi-international-408-vo-wes-1014x570.jpg)